Here i am describe All information about Trading.
Basics of Trading: A Beginner’s Guide
Trading involves buying and selling financial assets like stocks, bonds, commodities, or currencies with the aim of profiting from price fluctuations. It can be a complex endeavor, but understanding the fundamentals is crucial for success.
Key Concepts
- Asset: A financial instrument that can be bought, sold, or traded. Examples include stocks, bonds, commodities, currencies, and derivatives.
- Market: A platform where buyers and sellers come together to exchange assets.
- Bull Market: A market characterized by rising prices.
- Bear Market: A market characterized by falling prices.
- Volatility: The degree of variation in a financial instrument’s price over time.
- Liquidity: The ease with which an asset can be bought or sold without affecting its price.
Types of Trading
- Day Trading: Buying and selling assets within a single trading day.
- Swing Trading: Holding positions for a few days or weeks to capitalize on short-term price swings.
- Position Trading: Holding positions for several months or even years, focusing on long-term trends.
Fundamental Analysis vs. Technical Analysis
- Fundamental Analysis: Involves analyzing a company’s financial statements, industry trends, and economic factors to determine its intrinsic value.
- Technical Analysis: Focuses on chart patterns, historical price data, and technical indicators to predict future price movements.
Risk Management
- Stop-Loss Order: An order to sell a security when it reaches a specific price, limiting potential losses.
- Take-Profit Order: An order to sell a security when it reaches a specific price, securing profits.
- Diversification: Spreading investments across different asset classes to reduce risk.
Essential Tips for Beginners
- Start Small: Begin with a small investment to gain experience.
- Educate Yourself: Continuously learn about the market and trading strategies.
- Practice with a Demo Account: Test your strategies without risking real money.
- Develop a Trading Plan: Define your goals, risk tolerance, and trading strategy.
- Emotional Control: Avoid impulsive decisions based on fear or greed.
- Stay Disciplined: Stick to your trading plan and avoid overtrading.
Remember, trading involves risks. It’s crucial to do thorough research, manage risk effectively, and be patient. Consider consulting with a financial advisor before making significant investment decisions.
Would you like to delve deeper into a specific aspect of trading, such as technical analysis, fundamental analysis, or risk management?
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Asset | A financial instrument that can be bought, sold, or traded. Examples: stocks, bonds, commodities, currencies, and derivatives. |
| Market | A platform where buyers and sellers come together to exchange assets. |
| Bull Market | A market characterized by rising prices. |
| Bear Market | A market characterized by falling prices. |
| Volatility | The degree of variation in a financial instrument’s price over time. |
| Liquidity | The ease with which an asset can be bought or sold without affecting its price. |
Fundamental Analysis vs. Technical Analysis
| Type | Definition |
|---|---|
| Fundamental Analysis | Analyzing a company’s financial statements, industry trends, and economic factors to determine its intrinsic value. |
| Technical Analysis | Focusing on chart patterns, historical price data, and technical indicators to predict future price movements. |
Advance level Trading information.
Advanced Trading Strategies
- Options Trading:
- Call Options: The right to buy an asset at a specific price (strike price) within a certain timeframe.
- Put Options: The right to sell an asset at a specific price within a certain timeframe.
- Strategies:
- Covered Calls: Selling call options on a stock you already own.
- Protective Puts: Buying put options to protect against potential losses in a stock position.
- Straddles: Buying both a call and a put option on the same underlying asset with the same strike price and expiration date.
- Futures Trading:
- Contracts to buy or sell a specific asset at a future date at a predetermined price.
- Used to hedge risk, speculate on price movements, or arbitrage opportunities.
- Algorithmic Trading:
- Using computer programs to execute trades automatically based on predefined rules and algorithms.
- High-frequency trading (HFT): A type of algorithmic trading that involves executing a large number of trades at extremely high speeds.
- Arbitrage Trading:
- Capitalizing on price differences between two or more markets.
- Often involves complex strategies and sophisticated trading systems.
- Statistical Arbitrage:
- Identifying statistical relationships between different assets to exploit pricing inefficiencies.
Advanced Technical Analysis
- Elliott Wave Theory: Analyzing market cycles and trends based on a specific pattern of waves.
- Cyclical Analysis: Identifying long-term cycles in market prices.
- Volume Spread Analysis (VSA): Analyzing the relationship between price and volume to predict future price movements.
- Advanced Chart Patterns: More complex patterns like harmonic patterns, Gartley patterns, and butterfly patterns.
Advanced Risk Management Techniques
- Position Sizing: Determining the appropriate size of each trade based on risk tolerance and account balance.
- Risk Parity: Allocating capital to different assets based on their risk, rather than their expected return.
- Value at Risk (VaR): Estimating the potential loss in a portfolio over a specific time period with a certain confidence level.
- Conditional Value at Risk (CVaR): Measuring the expected loss beyond the VaR level.
Advanced Trading Psychology
- Emotional Discipline: Controlling emotions like fear, greed, and impatience.
- Risk Tolerance: Understanding and managing personal risk tolerance.
- Adaptability: Adjusting to changing market conditions and evolving trading strategies.
- Self-Awareness: Recognizing personal biases and limitations.
7 advanced trading tools traders need today:
1. Flexible Trade Automation
To get the most out of today’s shifting markets, empower your traders to focus on the things that matter most.
Especially for trading desks struggling with headcount, using automated trading capabilities like algo wheels and automated order routing to trade low-touch orders is an excellent way to free up traders’ time and get orders to market fast.
When your traders no longer need to focus on these simple, automatable trades, they can spend more time doing what they do best: fostering relationships, finding opportunities to capture more alpha, and working more complex trades.
This focus on more complex trading makes better use of their time and helps keep them engaged and committed to their jobs.
2. Fast and Streamlined Access to Liquidity
Cumbersome or manual trading workflows slow down processes and may cause you to miss opportunities as they arise.
Technology that provides centralized access to multi-broker aggregated liquidity and tools enables traders to dynamically manage positions, portfolios, and trading risk across global equity, futures, and options markets.
Moreover, features that support fast and streamlined access to liquidity – like algo wheels and “hot keys” – help to get orders out to market in less clicks.
3. Integrated Compliance Functionality
Compliance looms over every market, but in fast-moving markets with high volumes, compliance becomes even more challenging, and the last thing you want is cumbersome compliance workflows slowing down your trades.
You need a system that integrates compliance functionality right into your trading workflow. This level of integration keeps traders happy with smooth-flowing trades while also satisfying the evolving requirements of your compliance team.
4. Best Execution Measurment and Transaction Cost Analysis (TCA)
In volatile markets, knowing if and when you are trading efficiently and effectively can often take time and effort.
Technology is a vital resource for helping you understand your performance. Systems with built-in best execution measurement tools like charting and market fragmentation can track and monitor your performance and help you stay on top of your obligations.
Moreover, your system should be able to integrate with third-party TCA providers. These providers can ingest your data and offer valuable insight.
5. Scalability
The ups and downs of the market mean you need to be able to capture opportunities as they arise. Doing so requires technology you can depend on to meet your needs today and scale to secure new opportunities in the future.
Ideally, your technology provider offers a wide breadth of solutions you can deploy modularly to meet your needs as you grow. An investment ecosystem, for example, extends the value of your technology by enabling you to access and deploy new solutions faster than ever before.
I prefer some books for trading – checkout below books for beginners!


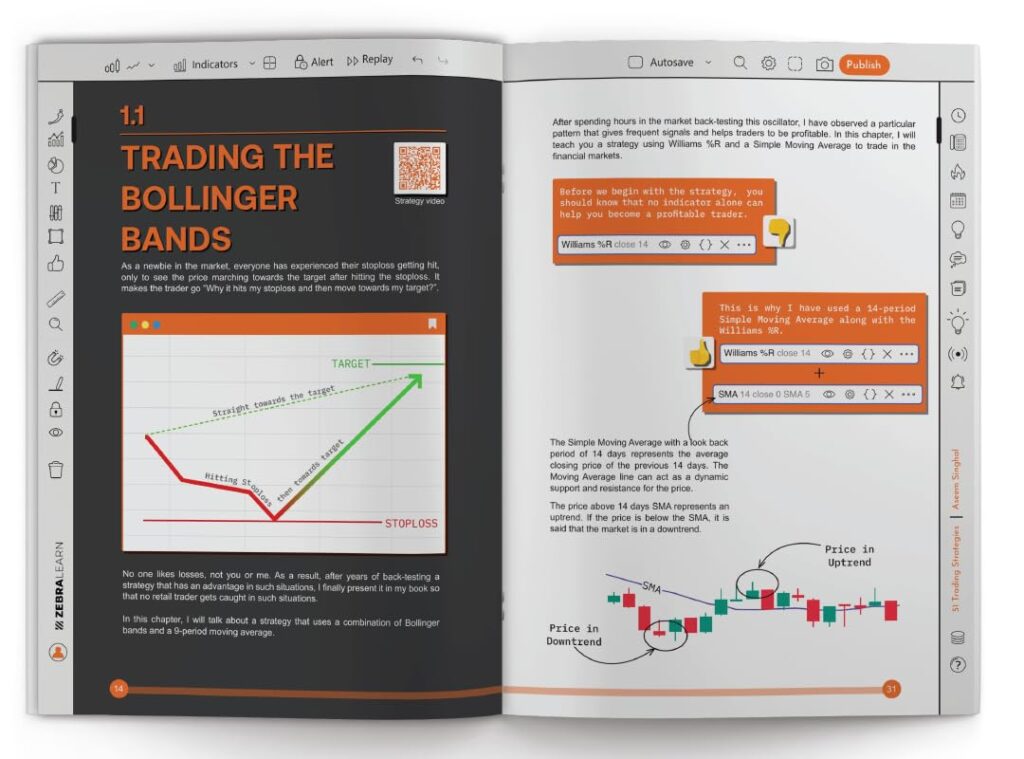
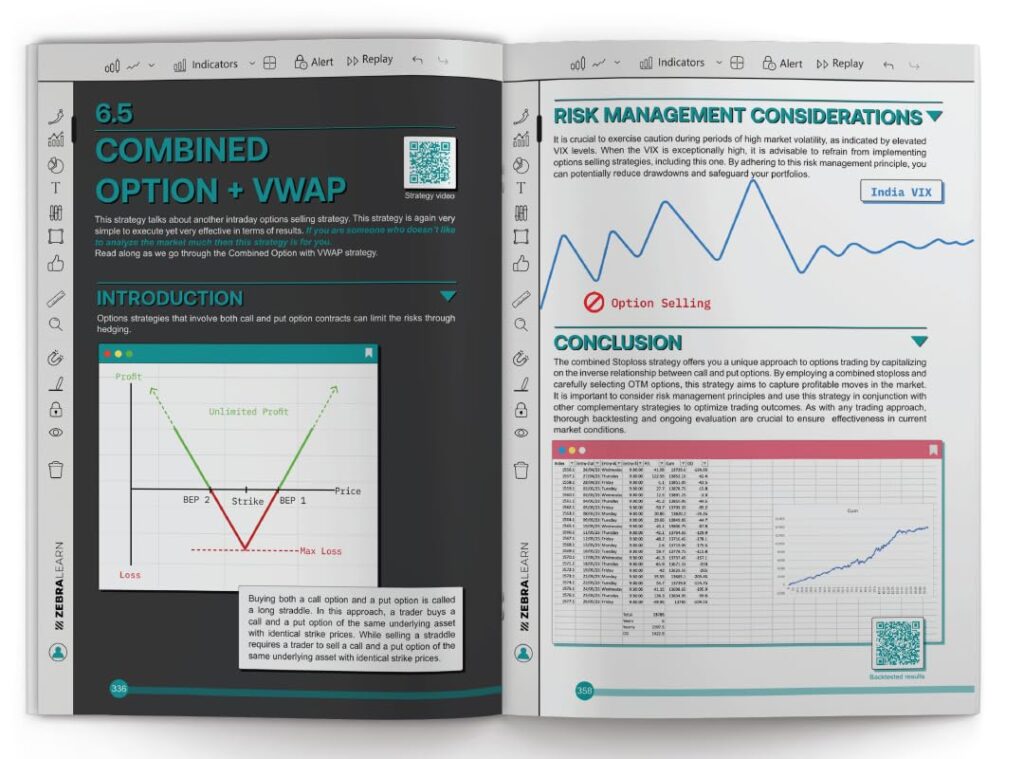
51 Trading Strategies is an ultimate trading guide for beginner and intermediate Traders to master 51 distinct strategies that span across various trading styles, methodologies, and philosophies, whether you’re a swing trader, intraday trader, positional trader, or scalping enthusiast. Explore Strategies based on swings, Intraday, Dow Theory, Positional, Time frames, Scalping, Options & Price Action. These strategies are recommended and tested by the Author through years of experience. This book is not about theory, it’s a trading walk-tour, to give you a real-time learning experience. This book is about getting results. Throughout this book, we back our strategies with historical data and backtested results. Based on these performance metrics you will have confidence while executing them in real markets. For all 51 strategies, you will find an explainer, how to buy, how to sell, risk management, backtested results and performance supported by real-world examples and practical tips. By the end, you’ll have the tools to improve your trading performance, adapt to market dynamics, maintain consistency, and manage risk effectively.
Posts
- India's GDP Growth Highlights: It Slows to 5.4% in Q2 FY25 (29/11/2024)
- what Next? Will Bank Nifty Sustain Gain on Monday? (24/11/2024)
- Tomorrow Market outlook - Monday Market Levels 2024 (17/11/2024)
- Market Rollercoaster: Indices Struggle to Gain Traction (11/11/2024)
- Market Crash Fears: Sensex, Nifty Plummet (07/11/2024)
- "US Election 2024: Trump vs Harris | Politico" (05/11/2024)
- Nifty 50 Weekly Outlook: Strategies Amid Global Volatility (03/11/2024)
- Overwhelming content created using AI in 2024 has tested customer confidence. (02/11/2024)
- Top 11 Stocks for Samvat 2081 with 15-20% Upside (31/10/2024)
- शेयर बाजार आज: निजी बैंक शेयरों में गिरावट के कारण निफ्टी 50, सेंसेक्स में 2 दिन की तेजी खत्म हुई (30/10/2024)
- Trending stocks today (29/10/2024)
- Why Did the Stock Market Crash Today? Breaking Down the Iran-Israel War and Sebi F&O Impact (28/10/2024)
Pages
- Trading Course (12/11/2024)
- Tech Information (04/11/2024)
- Shop (31/10/2024)
- Shop (31/10/2024)
- Latest News (27/10/2024)
- About (27/10/2024)
- Contact (27/10/2024)
- Services (27/10/2024)
- Home (27/10/2024)
- Services (26/10/2024)
- Cart (26/10/2024)
- Privacy Policy (26/10/2024)
Products
Nekit Mega Menu
- Mega Menu (12/11/2024)
